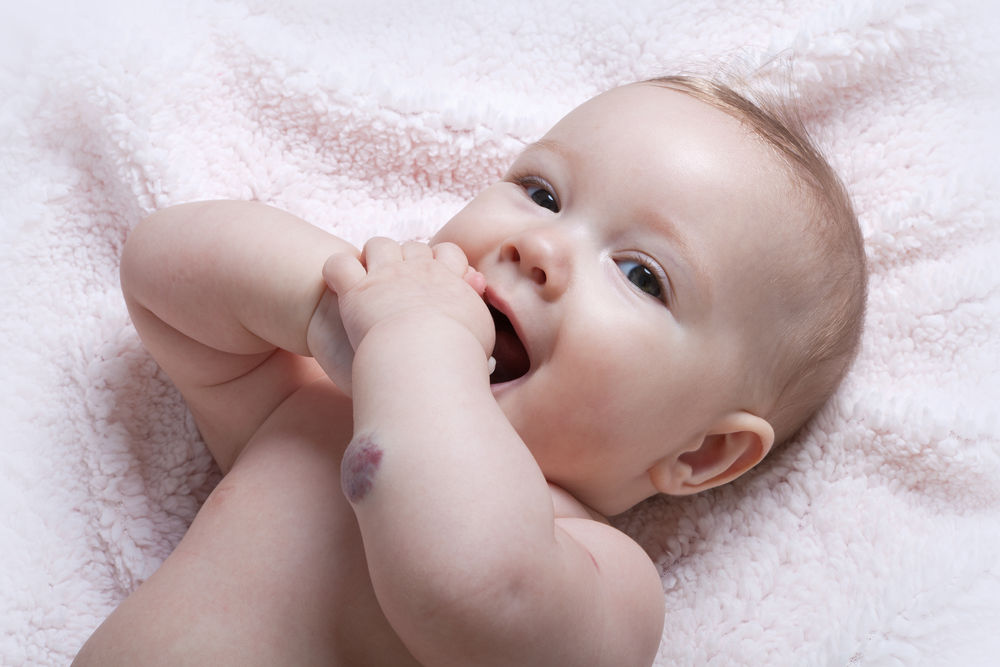

Birthmarks are generally either red or brown, caused by irregularities in the capillaries or vessels that supply blood to the skin.
Red marks are made up of lots of tiny blood vessels, whilst brown ones are made up of brown pigment (melanin).These vary greatly in size and occur in different parts of the body.Facial birthmarks are common and cause the most concern to patients.
Most birthmarks are harmless; many fade on their own in the first few years of life. But some vascular birthmarks can grow larger and more pronounced over time.
Alternative Names:
Strawberry mark; Vascular skin changes; Angioma cavernosum; Capillary hemangioma; Hemangioma simplex
Causes:
- Extensive development of blood vessels at the site.
- Moles present as birthmarks are due to abnormalities in the pigment cells in the skin known as melanocytes.
Symptoms:
- Skin markings that develop before or shortly after birth
- Skin rash or lesion that is red
- Skin markings look like a blood vessel
Red Birthmarks Treatment
- Many capillary birthmarks are temporary and require no treatment.
- The nevus flammeus type of hemangiomas may require no treatment unless they are disfiguring or psychologically distressing, or unless they develop new qualities like becoming painful or changing appearance.
- Permanent lesions may be disguised with cosmetics, especially cosmetics designed to be concealing or covering (such as Covermark).
- Oral or injected cortisone may be used to reduce the size of a hemangioma that is growing rapidly and obstructing vision or vital structures.
- Permanent birthmarks may be treated with cryotherapy (freezing), surgical removal, or laser surgery. They are usually not treated unless they cause unwanted symptoms, or until a child is at least school age.
- However, port wine stains on the face should be treated at a young age with a yellow pulsed dye laser for best results and to prevent the often profound psychosocial problems caused by the port wine stain.

The Laser Option
Red birthmarks are effectively treated with the Versapulse Laser, which progressively shrinks blood vessels causing the birthmark to fade. This revolutionary laser system is the equivalent of four lasers in one. Flat birthmarks tend to respond better than raised ones, although even in this latter group it is worthwhile having a test treatment. Multiple treatments are required
The variable pulse width 532 nanometre wavelength laser is responsible for treating unwanted blood vessels.The laser light targets the haemoglobin in the very superficial blood vessels and causes the vessels to shrink over a period of 6 to 8 weeks.The pulse width can be varied to accommodate different sized vessels. A significant advantage of this laser is the absence of deep purple bruising after treatment which is seen with the Candela laser.
The skin is protected by us of a special chilled tip attached to the handpiece as well as the prior application of a gel to the skin. During treatment a stinging sensation is felt, but this can be lessened with the use of an anaesthetic cream if necessary.
After treatment the skin is generally blotchy and some areas of blistering or swelling may be noted. The Versapulse Laser does not cause bruising, so treatment is easy to conceal
In the treatment of brown pigment, the different lasers may be used for their ability to penetrate to differing depths in the skin to reach the pigment being treated.